How soon will things get better?
Posted by Elena del Valle on January 13, 2010
Click on image to enlarge
Graphic: Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
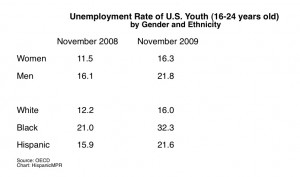
With an additional 85,000 jobs lost in the United States last month there is no doubt that joblessness has become the leading and most serious indicator of our nation’s economic crisis. According to a recent The New York Times article, as of December 2009 most unemployed Americans remain in that state for 29 weeks, the longest since the government began tracking that data in 1948. In order just to keep pace with new arrivals into the workforce the country needs 100,000 new jobs a month. There simply are not enough jobs. Worst of all there is no prospect of enough new jobs developing anytime soon. Are things getting better elsewhere?
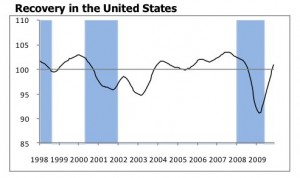
At the end of last week the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) which tracks changes in 29 countries announced its composite leading indicators or CLIs for November 2009 point to “stronger signals for recovery than last month’s assessment.” Researchers calculated CLIs for 29 OECD countries and 9 zones.
Analysts at the Paris-based organization interpret the new data to indicate an upward movement in the index of industrial production for the seven countries they examined, except Canada and the United Kingdom. The release also indicates that the CLIs for those major seven countries (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, United Kingdom and United States) moved above their long-term trend, indicating “an expansionary outlook relative to trend.” The organization’s data for major non member countries economies points to a recovery.
Specifically, the CLI for the OECD area increased by 1.0 point in November 2009 and was 8.2 points higher than in November 2008. The CLI for the United States increased by 1.0 point in November, 6.8 points higher than a year earlier. The Euro area’s CLI increased by 1.1 point in November, 10.9 points higher than a year ago. The CLI for Japan increased by 1.2 point in November, 5.4 points higher than a year ago.
The CLI for the United Kingdom increased by 1.2 point in November 2009, 10.7 points higher than a year ago. The CLI for Canada increased by 1.0 point in November, 9.4 points higher than a year ago. The CLI for France increased by 1.2 point in November, 11.9 points higher than a year ago. The CLI for Germany increased by 1.4 points in November, 12.3 points higher than a year ago. The CLI for Italy increased by 0.9 point in November, 13.8 points higher than a year ago.
The CLI for China increased 0.2 point in November 2009, 7.6 points higher than a year ago. The CLI for India is remained the same in November and 4.3 points higher than a year ago. The CLI for Russia increased by 1.0 point in November, 3.4 points higher than a year ago. The CLI for Brazil increased by 0.8 point in November, 1.3 points lower than a year ago.
What these numbers mean to everyday people in practical terms is anyone’s guess. For now, it seems to offer a small glimmer of hope that the famous V shape of the economic trend is moving up and away from the bottom in some countries.
OECD provides a forum for member governments to compare policy experiences, “seek answers to common problems, identify good practice and coordinate domestic and international policies.” The OECD-Total covers 29 countries: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Korea, Luxembourg, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovak Republic, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, United Kingdom, and United States. The Euro area (only Euro area countries that are members of OECD) covers 13 countries: Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Ireland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovak Republic and Spain. The Major Five Asia area covers China, India, Indonesia, Japan and Korea.